Project-based learning is a form of situated learning and is based on the constructivist finding that students gain deeper understanding of material when they actively construct their understand by working with and using ideas.
In project-based learning, students engage in real, meaningful problems that are important to them and similar to what scientists, mathematicians, writers and historians do. A project-based classroom allows students to investigate questions, propose hypotheses and explanations, discuss their ideas, challenge others’ ideas and try out new ideas.
The theoretical background of project-based learning is built on four major learning ideas.
Adapted from Krajcik JS, Blumenfeld PC. Project Based Learning at Sawyer, R. (Ed.). (2014). The Cambridge Handbook of the Learning Sciences (2nd ed., Cambridge Handbooks in Psychology). Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. doi:10.1017/CBO9781139519526
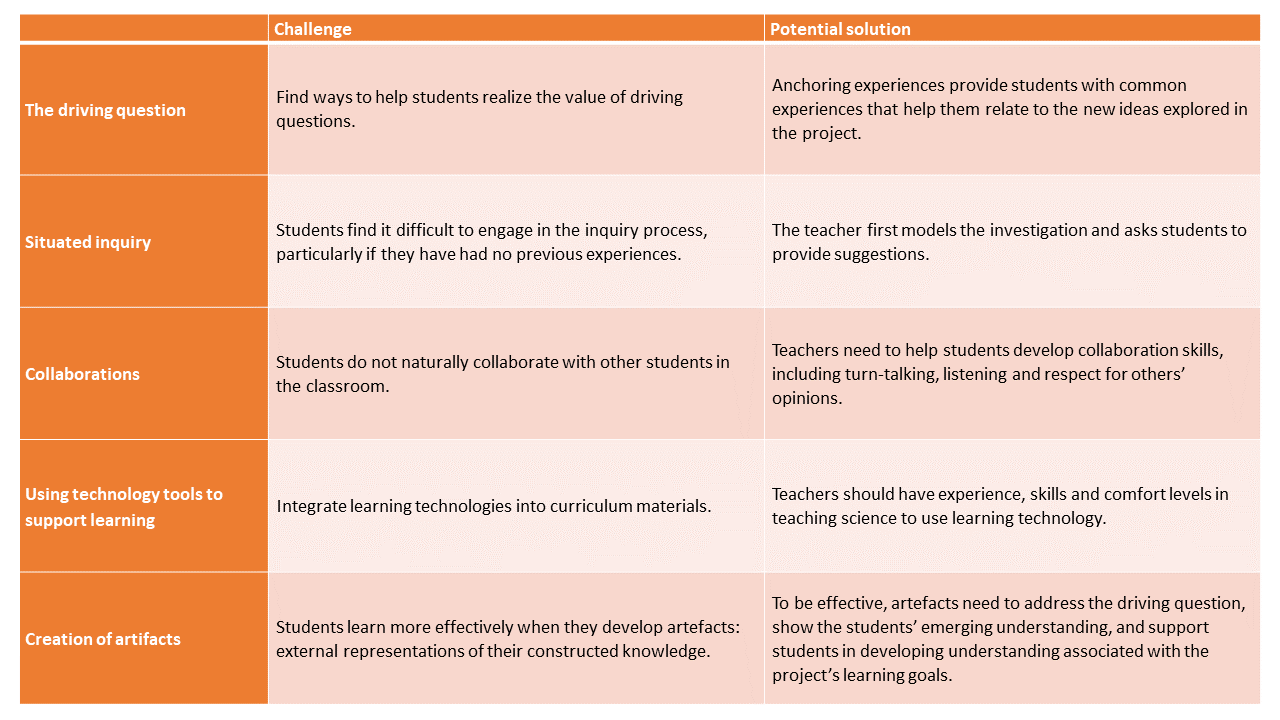
Table. Challenges and opportunities of Project-Based learning
Adapted from Krajcik JS, Blumenfeld PC. Project Based Learning at Sawyer, R. (Ed.). (2014). The Cambridge Handbook of the Learning Sciences (2nd ed., Cambridge Handbooks in Psychology). Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. doi:10.1017/CBO9781139519526